By the late 1970s Western analysts had identified a new fighter under developement for the Soviet Air Force. Since its first sighting at the Ramenskoye test range in 1977, when it got unofficially dubbed with the rather tentative and anonymous RAM-L designation, the Fulcrum has been one of the key aircraft on the military aviation scene. The twin-finned air superiority fighter, now known as the MiG-29, first flew in 1977 and entered service with Soviet fighter regiments in 1983.
In contrast to the primitive electronics of the MiG-25, the MiG-29 has a radar system comparable to wome Western machines. Like the post-Vietnam generation of US fighters, it was an agile aircraft capable of maneuvering in a dog-fight. The MiG-29 was marketed worldwide and equaled or surpassed the F-15C in several areas. Consequently, the MiG-29 was initially a useful export fot the new Russian Republic, though subsequently it was eclipsed by the larger Su-27.
 The MiG-29 is superficially similar in layout to the larger Su-27, and unlike counterpart American fighters which are easily distinguished, a close attention to design details is needed to distinguish the two Russian fighters:
The MiG-29 is superficially similar in layout to the larger Su-27, and unlike counterpart American fighters which are easily distinguished, a close attention to design details is needed to distinguish the two Russian fighters:
- The most striking difference is the Su-27's signature centerline fuselage stinger, which protrudes well aft of the engine exhaust, and is entirely absent on the MiG-29, though this feature may not be apparent from all angles.
- The vertical stabilizers on the MiG-29 are canted outward, while those of the Su-27 are vertical.
- Conversely, the air intakes on the MiG-29 are canted inward, while the air intakes on the Su-27 are vertical.
- The Mig-29 fuselage sits entirely above the air intakes, engine pods and exhaust beneath the wings, whereas on the Su-27 there is a distinct droop of the forward fuselage below the upper edges of the air intakes.
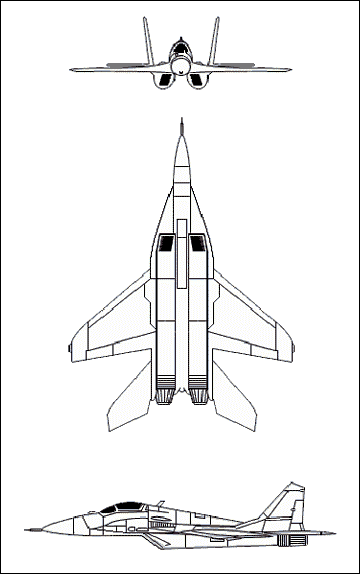
The MiG-29's wings are swept-back and tapered with square tips. The Leading- Edge Root Extensions (LERXs) are wide and curved down to the front. LERX begins on the nose below the mid-mount point, and the wings’ trailing edges end at a high-mounted point. Twin jet engines are mounted low and to the sides of the fuselage. Diagonal-shaped air intakes give a box-like appearance, with large exhausts. The fuselage is made of a long, thin, slender body with long, pointed drooping nose. There is a high-mounted bubble canopy. The tail fins have sharply tapered leading edges, canted outward with angular, cutoff tips. Flats are high-mounted on the fuselage, movable, swept-back, and tapered with a negative slant.
There are half a dozen major variants of the MiG-29 recognized under the NATO reporting name taxonomy, while MiG itself accounts for variants too numerous to enumerate.
- Fulcrum-A - MiG-29 basic version
- Fulcrum-B - MiG-29UB two-seat conversion trainer
- Fulcrum-C - MiG-29S bulged and extended spine houses both fuel and avionics
- Fulcrum-D - MiG-29K/ MiG29KUB navalized for carrier ops
- Fulcrum-E - MiG-29M wide-ranging upgrades, did not enter production
- Fulcrum-F - Mig-29OVT/ MiG-35 thrust-vector control engine
The MiG-29 basic version fighter is capable of hitting air targets day and night, in any weather, in free airspace and against the earth background and in active and passive jamming environment. The MiG-29 fighter (export version B) is armed with R-27R1 medium-range missiles with semi-active radar homing heads and R-73E short-range missiles, and unguided weapons (S-24B and S-8 rockets and FAB-250 and FAB-500 free-fall bombs) for hitting ground and sea-surface targets. The aircraft also has a built-in GSh-301 gun (30 mm caliber).
The MiG-29 has a few advantages over its more electronically advanced American counterparts. At about 40 miles apart, the American planes have the advantage because of avionics. At 10 miles the advantage is turning to the MiG. At five miles out, because of the MiG weapons sight and better maneuverability, the advantage is to the MiG. The weapons sight is a helmet-mounted system that allows the missile to follow the line of sight of the pilot's helmet. Where the pilot looks is where it goes.
The MiG-29 is a widely exported aircraft, flown by Iraq, Iran, North Korea, India, Syria, Cuba and Afghanistan, as well as Czechoslovakia, East Germany and Yugoslavia. Aside from MiG-29 basic version B, other modifications of the MiG-29 family, such as MiG-29SE, MiG-29SD, MiG-29SM and MiG-29SMT, can be offered to customers. Moreover, the MiG-29 fighters operated by customers can be upgraded to the level of the SE, SD, SM and SMT versions. The MiG-29UB aircraft and its modifications are manufactured by "Sokol" Joint-Stock Company of Nizhny Novgorod.
MiG Corp. offers its customers three basic versions - the MiG-29SD, MiG-29SM and MiG- 29SMT. They significantly differ from each other in terms of functionality and price. The MiG-29SD is an air superiority fighter adapted for NATO/ ICAO standards. Its advanced version, the MiG-29SM, is a cost-effective multi-role aircraft. Finally, the MiG-29SMT is a generation 4+ fighter equipped with new targeting system, avionics and armament.
The US Department of Defense of the United States of America and the Ministry of Defense of the Republic of Moldova reached an agreement to implement the Cooperative Threat Reduction accord signed on June 23, 1997, in Moldova. The Pentagon pounced on the planes after learning Iran had inspected the jets and expressed an interest in adding them to their inventory. Although Iran already flew the less-capable Fulcrum A, it doesn't own any of the more advanced C-models. Of the 21 Fulcrums the United States bought, 14 are the frontline Fulcrum C's, which contain an active radar jammer in its spine, six older A's and one B-model two-seat trainer. This agreement authorized the United States Government to purchase nuclear-capable MiG-29 fighter planes from the Government of Moldova. This was a joint effort by both Governments to ensure that these dual-use military weapons do not fall into the hands of rogue states. From Oct. 20 to Nov. 2, 1997, loadmasters and aerial port experts squeezed two MiGs apiece, sans wings and tails, into the cargo holds of C-17 Globemaster III transports from Charleston Air Force Base, SC. The Charleston airlifters delivered the MiGs to the National Air Intelligence Center at Wright-Patterson AFB near Dayton, Ohio. If NAIO can discover how the Fulcrum works, Air Force pilots might gain an edge if they faced the Fulcrum in future combat.

The MiG-29 upgrade project involves two main packages for customers. The first package offers the full upgrade of the aircraft up to the MiG-29SMT level. The second package offers the upgrade of certain aircraft units and aggregates and installation of new completing elements (including those of Western produce) to suit customers' requirements. In the process of upgrade, some share of contract works could be transferred to the aviation plants of the customer's country.
Improvement of aircraft performance includes: increase of flight range, improvement of aircraft maneuverability and upgrade of engines. An increase of the flight range up to 3,000 km can be reached by installation of additional 1800 l conformal tanks. Installation of the in-flight refueling system makes it possible to use both Russian and Western tankers. Due to installation of three external fuel tanks and in-flight refueling system, the aircraft flight range can be increased up to 6200 km;
The RD-33 engine upgrade provides for the thrust-vector control and increase of engine thrust and fuel efficiency. The core upgrade of the engine itself is now at the test bench stage and should be completed in the nearest future. The installation of these engines will enhance the aircraft power-to-weight ratio to the level of fifth-generation aircraft. All these characteristics will allow the operator to keep the aircraft air superiority till 2010-2015.
The aircraft was criticized for the low assigned lifetime (2,500 hours only). However, the operation of the aircraft produced in early 1980s have demonstrated that the lifetime could be extended to 4,000 hours in the event they are maintained properly. This allows extension of their lifetime till 2010-2015. The practice of overhauls has also been revised. Transition to on-condition maintenance has been adopted. The calculations have shown that the operating cost of one air vehicle can be reduced by 15-20% if 4000 hour lifetime is assigned and transition to on-condition maintenance is performed. The worked to increase the engine lifetime have been carried out.
 |  |
 |  |
At MAKS-2003 airshow MiG Corp. presented, along with the basic version of MiG-29, its newest modifications – MiG-29K, MiG-29M2, MiG-29SMT, MiG-29OVT. MiG-29K/KUB and MiG-29M/M2 belong to a family of multirole single/twin-seater ship and shore-based fighters accordingly. Aircraft designs are unified up to 90%. Such approach gives several advantages. Serial production becomes cheaper thus influences market price of the aircraft. Exploitation, maintenance and logistics support system as well as the system of pilots and ground personnel training become simpler. The fleet of aircraft in the Air Force can become more unified. All this, along with flight-technical and combat characteristics, makes MiG-29 family quite attractive for potential customers.
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight | (MiG-29) 6 October 1977 (MiG-29M) 1989 (MiG-29UBT) 8 October 1998 |
| Service Entry | 1983 |
| CREW: | 1 pilot |
| ESTIMATED COST: | unknown |
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | unknown |
| Wing Tip | unknown |
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length | 56.83 ft (17.32 m) |
| Wingspan | 37.29 ft (11.36 m) |
| Height | 15.54 ft (4.73 m) |
| Wing Area | 408 ft2 (38.0 m2) |
| Canard Area | not applicable |
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty | 24,030 lb (10,900 kg) |
| Typical Load | 33,600 lb (15,240 kg) |
| Max Takeoff | 40,785 lb (18,500 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity | internal: unknown external: unknown |
| Max Payload | 6,614 lb (3,000 kg) |
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant | (MiG-29A) two Klimov/ Sarkisov RD-33 afterburning turbofans (MiG-29M) two Klimov/ Sarkisov RD-33K afterburning turbofans |
| Thrust | (RD-33) 36,600 lb (162.8 kN) (RD-33K) 41,450 lb (184.44 kN) |
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed | at altitude: 1,520 mph (2,445 km/h) at 36,090 ft (11,000 m), Mach 2.3 at sea level: 805 mph (1,200 km/h), Mach 1.06 |
| Initial Climb Rate | 65,000 ft (19,800 m) / min |
| Service Ceiling | 60,700 ft (18,500 m) |
| Range | typical: 810 nm (1,500 km) 340 nm (630 km) with max payload ferry: 1,570 nm (2,900 km) |
| g-Limits | unknown |
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun | one 30-mm GSh-301 cannon (150 rds) |
| Stations | six or seven external hardpoints (MiG-29K) nine external hardpoints (MiG-29M) eight external hardpoints |
| Air-to-Air Missile | R-60/AA-8 Aphid, R-27/AA-10 Alamo, R-73/AA-11 Archer, R-77/AA-12 Adder |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | AS-12, AS-14, AS-17 |
| Bomb | free-fall, guided, cluster bombs |
| Other | rocket pods, ECM pods, munitions dispensers |
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| 9-01 | Pre-production model |
| MiG-29 'Fulcrum-A' | First production model, prototypes included three slightly different models with varying types of nose gear, fin, and rudder arrangements |
| MiG-29UB 'Fulcrum-B' | Two-seat trainer with radar removed |
| MiG-29S 'Fulcrum-C' | Improved single-seat fighter for serial production with an enlarged fuselage, new avionics, and a larger fuel capacity |
| MiG-29KVP | MiG-29K prototype built to test catapult takeoff and arrestor gear systems, may also have been used as a trainer for the MiG-29K |
| MiG-29K 'Fulcrum-D' | Navalized one-seat multipurpose fighter for use on aircraft carriers; Russian production cancelled after trials completed but a derivative was later purchased by India |
| MiG-29KU | Trainer version of the MiG-29K with a modified nose adding a separate cockpit for the instructor forward and below the normal cockpit; cancelled |
| MiG-29KUB | Trainer version of the MiG-29K purchased by India and the Russian Navy |
| MiG-29B | Two-seat version, details unknown |
| MiG-29UBT | Two-seat strike model designed for special operations |
| MiG-29SD | Export version of the MiG-29S |
| MiG-29SE | Export version of the MiG-29S with a new ECM jammer |
| MiG-29N | Export version for Malaysia similar to the MiG-29SD and optimized for air defense but equipped with in-flight refueling capability, updated communications equipment, improved navigation systems, and updated engines |
| MiG-29UBN | Two-seat trainer exported to Malaysia |
| MiG-29SM | Improved MiG-29S/SE with in-flight refueling capability, increased payload, and the ability to carry improved air-to-air missiles plus a TV display compatible with the KAB-500KR guided bomb or the Kh-29T missile, also capable of carrying the Kh-31A and Kh-31P missiles |
| MiG-29SMT | Modernization program for MiG-29SM export models with an improved cockpit, improved avionics, and increased range |
| MiG-29SMT-2 | "Second stage" modernization program for export models that provides a new radar, improved engines, revised ECM equipment, a digital fly-by-wire control system, and compatibility with numerous adbanced air-to-air and air-to-surface weapons |
| MiG-29SMTK | Carrier-based export model offered to India, includes folding wings, arrestor gear, and improved navigation systems |
| MiG-29M 'Fulcrum-E' | Improved fighter with fly-by-wire controls, upgraded engines, a modified tail and wing layout, a revised canopy, and the ability to carry guided-munitions |
| MiG-29MaE or MiG-29MEh or MiG-29EM | Export version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29MR | Reconnaissance version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29UM | Two-seat combat-capable trainer version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29M2 'Fulcrum-F' | Two-seat variant of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29 'Fulcrum-Plus' | MiG-29 variant equipped with thrust-vectoring nozzles and canards, not believed to have been completed or flown due to financial problems |
| MiG-29OVT | Early designation for the MiG-35 |
| MiG-29AS | Upgrade program for single-seat MiG-29 fighters used by Slovakia that includes installation of new IFF equipment and American radios while also adding an improved navigation system; 10 converted |
| MiG-29UBS | Upgrade program for MiG-29UB trainers used by Slovakia; 2 converted |
| MiG-33 | Believed to be a designation for an export version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-35 | Upgraded model based on the MiG-29M2 primarily for the export market |
| KNOWN COMBAT RECORD: | Iraq - Operation Desert Storm (Iraq, 1991) Chechnya (Russia, 1994-present) Bosnia - Operation Deliberate Force (Serbia, 1995) Kosovo - Operation Allied Force (Serbia, 1999) |
| KNOWN OPERATORS: | Algeria, Al Quwwat al Jawwawiya al Jaza'eriya (Algerian Air Force) Angola, Força Aérea Popular de Angola (Angolan People's Air Force) Armenia (Armenian Air Force) Azerbaijan (Azerbaijan Air Force) Bangladesh, Bangladesh Biman Bahini (Bangladeshi Defense Force Air Wing) Belarus, Voyenno Vozdushnyye Sily (Belarus Air Force) Bulgaria, Bulgarski Voenno Vozdushni Sili (Bulgarian Air Defense Force Military Aviation) Croatia, Hrvatske Zracne Snage (Croatian Air Force) Cuba, Defensa Antiaerea y Fuerza Aérea Revolucionaria (Anti-Aircraft Defense and Revolutionary Air Force) Czechoslovakia, Ceskoslovenske Letectvo (Czechoslovak Air Force) Czech Republic, Cesk Letectvo a Protivzbusna Obrana (Czech Air Force and Air Defense) East Germany, Luftstreitkräfte/Luftverteidigung (Air Force/Air Defense Force) Germany, Deutsche Luftwaffe (German Air Force) Hungary, Magyar Légierö (Hungarian Red Air Arm) Hungary, Magyar Honvedseg Repülö Csapatai (Hungarian Air Defense Group) India, Bharatiya Vayu Sena (Indian Air Force) India (Indian Naval Air Squadron) Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force) Iraq, Al Quwwat Al Jawwiya al Iraqiya (Iraqi Air Force) Kazakhstan (Kazakhstan Air Force) Lebanon, Al Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Lubnamia (Lebanese Air Force) Malaysia, Tentera Udara Diraja Malaysia (Royal Malaysian Air Force) Moldova (Moldovan Air Force) North Korea (Korean People's Army Air Force) Peru, Fuerza Aérea del Perú (Peruvian Air Force) Poland, Sily Powietrzne Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej (Polish Air Force) Poland, Polska Wojska Lotnicze i Obrony Powietrznej (Polish Air Defense and Aviation Force) Romania, Fortele Aeriene Române (Romanian Air Force) Russia, Voyenno Vozdushniye Sili (Russian Air Force) Russia, Aviatsiya Voyenno-Morskoyo Flota Sily Rossii (Russian Naval Aviation) Serbia, Vazduhoplovstvo i PVO Vojske Srbije (Serbian Air Force) Slovakia, Velitelstvo Vzdusnych Sil (Slovak Air Force) Sri Lanka (Sri Lankan National Air Force) Sudan, Silakh al Jawwiya As'Sudaniya (Sudanese Air Force) Syria, Al Quwwat al-Jawwiya al Arabiya as-Souriya (Syrian Air Force) Turkmenistan, Voyenno-Vozdushneyye Sily (Turkmenistan Air Force) Ukraine, Viys'kovo-Povitriani Syly Ukrayiny (Ukraine Military Air Forces) Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, Voyenno Vozdushniye Sili (Soviet Air Force) Uzbekistan (Uzbek Air Force) Yemen, Al Quwwat al Jawwiya al Yemeniya (Unified Yemen Air Force) Yugoslavia, Ratno Vazduhoplovstvo i Protiv Vazdusna Odbrana (Serbia and Montenegro Air and Air Defence Force) |
| 3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
 | |




0 komentar:
Posting Komentar